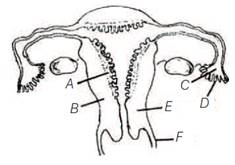
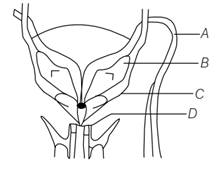
Chapter: Human Reproduction
0 of 90 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
Information
Subject: Biology
Syllabus: Human Reproduction
Duration: 1 Hr.
Read the following instruction carefully.
- There are 90 total questions in this test
- Each question has 4 options out of which only one is correct.
- You will be awarded 4 points for each correct answer and 1 point will be deducted for each wrong answer.
- Try not to guess the answer as there is negative marking.
- Your Score & Rank will be shown after submitting the test.
- In this quiz you are going to check your conceptual knowledge.
You have already completed the Test before. Hence you can not start it again.
Test is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the Test.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this Test:
Your results are here!! for" NPY_12_Bio_25_03_Human Reproduction "
0 of 90 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
Your Final Score is : 0
You have attempted : 0
Number of Correct Questions : 0 and scored 0
Number of Incorrect Questions : 0 and Negative marks 0
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
-
Not categorized
You have attempted: 0
Number of Correct Questions: 0 and scored 0
Number of Incorrect Questions: 0 and Negative marks 0
-
Level 1 Single Answer Type
You have attempted: 0
Number of Correct Questions: 0 and scored 0
Number of Incorrect Questions: 0 and Negative marks 0
-
Dear $form{0} you have completed this test.
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 90
1. Question
4 pointsMatch the following columns and select the correct option.
Column I Column II
A. Placenta 1. Androgens
B. Zona pellucida 2. Human Chorinoic Gonadotropin (hCG)
C. Bulbourethral glands 3. Layer of the ovum
D. Leydig cells 4. Lubrication of the penis -
Question 2 of 90
2. Question
4 pointsSelect the correct sequence for transport of sperm cells in male reproductive system.
-
Question 3 of 90
3. Question
4 pointsWhich of the following depicts the correct pathway of transport of sperms?
-
Question 4 of 90
4. Question
4 pointsThe shared terminal duct of the reproductive and urinary system in the human male is
-
Question 5 of 90
5. Question
4 pointsThe Leydig cells as found in the human body are the secretory source of
-
Question 6 of 90
6. Question
4 pointsIf for some reason, the vasa efferentia in the human reproductive system get blocked, the gametes will not be transported from
-
Question 7 of 90
7. Question
4 points -
Question 8 of 90
8. Question
4 pointsThe testes in humans are situated outside the abdominal cavity inside a pouch called scrotum. The purpose served is for
-
Question 9 of 90
9. Question
4 pointsSertoli cells are found in
-
Question 10 of 90
10. Question
4 pointsVasa efferentia are the ductules leading from
-
Question 11 of 90
11. Question
4 pointsSeminal plasma in human males is rich in
-
Question 12 of 90
12. Question
4 pointsThe part of Fallopian tube closest to the ovary is
-
Question 13 of 90
13. Question
4 points -
Question 14 of 90
14. Question
4 pointsBartholin’s glands are situated
-
Question 15 of 90
15. Question
4 pointsLocation and secretion of Leydig’s cells are
-
Question 16 of 90
16. Question
4 pointsSelect the correct option of haploid cells from the following groups.
-
Question 17 of 90
17. Question
4 pointsMatch the following columns and select the correct option from the codes given belows
Column I Column II
- Ovary 1. Human chorionic gonadotropin
- Placenta 2. oestrogen and progesterone
- Corpus luteum 3. Androgens
- Leydig cells 4. Progesterone only
-
Question 18 of 90
18. Question
4 pointsWhich of the following hormone levels will cause release of ovum (ovulation) from the Graafian follicle?
-
Question 19 of 90
19. Question
4 pointsMeiotic division of the secondary oocyte completed
-
Question 20 of 90
20. Question
4 pointsNo new follicles develop in the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle because
-
Question 21 of 90
21. Question
4 pointsWhat is the fate of the male gametes discharged in the synergid?
-
Question 22 of 90
22. Question
4 pointsExtrusion of second polar body from egg nucleus occurs
-
Question 23 of 90
23. Question
4 pointsThe difference between spermiogenesis and spermiation is
-
Question 24 of 90
24. Question
4 pointsMatch the items given in Column I with those in Column II and select the correct option given below.
Column I Column II 1. Proliferative phase i. Breakdown of endometrial lining 2. Secretory phase ii. Follicular phase 3. Menstruation iii. Luteal phase -
Question 25 of 90
25. Question
4 pointsA temporary endocrine gland in the human body is
-
Question 26 of 90
26. Question
4 pointsSelect the incorrect statement.
-
Question 27 of 90
27. Question
4 pointsIdentify the correct statement on ‘inhibin’.
-
Question 28 of 90
28. Question
4 pointsChanges in GnRH pulse frequency in females is controlled by circulating levels of
-
Question 29 of 90
29. Question
4 pointsWhich of the following layers in an antral follicle is acellular?
-
Question 30 of 90
30. Question
4 pointsWhich of the following events in not associated with ovulation in human female?
-
Question 31 of 90
31. Question
4 pointsThe main function of mammalian corpus luteum is to produce
-
Question 32 of 90
32. Question
4 pointsWhat is the correct sequence of sperm formation?
-
Question 33 of 90
33. Question
4 pointsMenstrual flow occurs due to lack of
-
Question 34 of 90
34. Question
4 pointsWhich one of the following statements is false in respect of viability of mammalian sperm?
-
Question 35 of 90
35. Question
4 pointsWhich one of the following statements about human sperm is correct?
-
Question 36 of 90
36. Question
4 pointsWhich one of the following is the most likely reason of not occurring regular menstruation cycle in females?
-
Question 37 of 90
37. Question
4 pointsWhich one of the following is the correct matching of the events occurring during menstrual cycle?
-
Question 38 of 90
38. Question
4 pointsWhich one of the following statement is incorrect about menstruation?
-
Question 39 of 90
39. Question
4 pointsAt the end of first meiotic division, male germ cell differentiates into
-
Question 40 of 90
40. Question
4 pointsWhich part of ovary in mammals acts as an endocrine gland after ovulation?
-
Question 41 of 90
41. Question
4 pointsIf mammalian ovum fails to get fertilised, which one of the following is unlikely?
-
Question 42 of 90
42. Question
4 pointsOvulation in the human female normally takes place during the menstrual cycle
-
Question 43 of 90
43. Question
4 pointsWhich set is similar?
-
Question 44 of 90
44. Question
4 pointsMiddle piece of mammalian sperm possesses
-
Question 45 of 90
45. Question
4 pointsAfter ovulation, Graafian follicle regresses into
-
Question 46 of 90
46. Question
4 pointsIn 28 days human ovarian cycle, ovulation occurs on
-
Question 47 of 90
47. Question
4 pointsFertilisins are emitted by
-
Question 48 of 90
48. Question
4 pointsHuman eggs are
-
Question 49 of 90
49. Question
4 pointsOvulation occurs under the influence of
-
Question 50 of 90
50. Question
4 pointsIn telolecithal egg the yolk is found
-
Question 51 of 90
51. Question
4 pointsFreshly released human egg has
-
Question 52 of 90
52. Question
4 pointsEgg is liberated from ovary in
-
Question 53 of 90
53. Question
4 pointsThere is no DNA in
-
Question 54 of 90
54. Question
4 pointsReceptors for sperm binding in mammals are present on
-
Question 55 of 90
55. Question
4 pointsCapacitation occurs in
-
Question 56 of 90
56. Question
4 pointsFertilisation in humans is practically feasible only if
-
Question 57 of 90
57. Question
4 pointsEctopic pregnancies are referred to as
-
Question 58 of 90
58. Question
4 pointsIn human females, meiosis-II is not completed until
-
Question 59 of 90
59. Question
4 pointsSelect the correct option describing gonadotropin activity in a normal pregnant female
-
Question 60 of 90
60. Question
4 pointsWhich one of the following statements about morula in humans is correct?
-
Question 61 of 90
61. Question
4 pointsA change in the amount of yolk and its distribution in the egg will affect.
-
Question 62 of 90
62. Question
4 pointsGray crescent is the area
-
Question 63 of 90
63. Question
4 pointsWhat is true for cleavage?
-
Question 64 of 90
64. Question
4 pointsCleavage in mammalian egg is
-
Question 65 of 90
65. Question
4 pointsBlastopore is
-
Question 66 of 90
66. Question
4 pointsWhat is true about cleavage in fertilised egg of human?
-
Question 67 of 90
67. Question
4 pointsAcrosome reaction in sperm is triggered by
-
Question 68 of 90
68. Question
4 pointsExtrusion of second polar body from egg nucleus occurs
-
Question 69 of 90
69. Question
4 pointsTermination of gastrulation is indicated by
-
Question 70 of 90
70. Question
4 pointsMeroblastic cleavage is a type of division
-
Question 71 of 90
71. Question
4 pointsDuring cleavage, what is true about cells?
-
Question 72 of 90
72. Question
4 pointsHow many sperms are formed from a secondary spermatocyte?
-
Question 73 of 90
73. Question
4 pointsWhich of the following secretes the hormone, relaxin, during the later phase of pregnancy?
-
Question 74 of 90
74. Question
4 pointsWhich of these is not an important component of initiation of parturition in humans?
-
Question 75 of 90
75. Question
4 pointsIn human beings, at the end of 12 weeks (first trimester) of pregnancy, the following is observed.
-
Question 76 of 90
76. Question
4 pointsSelect the correct sequence of events
-
Question 77 of 90
77. Question
4 pointsWhich of the following hormones is responsible for both the milk ejection reflex and the foetal ejection reflex?
-
Question 78 of 90
78. Question
4 pointsColostrum, the yellowish fluid, secreted by mother during the initial days of lactation is veryessential to impart immunity to the new born infants because it contains
-
Question 79 of 90
79. Question
4 pointsThe amnion of mammalian embryo is derived from
-
Question 80 of 90
80. Question
4 pointsHormones secreted by the placenta to maintain pregnancy are
-
Question 81 of 90
81. Question
4 pointsMatch column I with column II and select the correct option using the codes given below.
Column I Column II
A. Mons pubis 1. Embryo formation
B. Antrum 2. Sperm
C. Trophecto derm 3. Female external genitalia
D. Nebenkern 4. Graafian follicle -
Question 82 of 90
82. Question
4 pointsSeveral hormones like hCG, hPL, oestrogen, progesterone are produced by
-
Question 83 of 90
83. Question
4 pointsWhich one of the following is not the function of placenta? It
-
Question 84 of 90
84. Question
4 pointsSignals for parturition originate from
-
Question 85 of 90
85. Question
4 pointsThe first movements of the foetus and appearance of hair on its head are usually observed during which month of pregancy?
-
Question 86 of 90
86. Question
4 pointsWhich extra-embryonic membrane in humans prevents desiccation of the embryo inside the uterus?
-
Question 87 of 90
87. Question
4 pointsDuring embryonic development, the establishment of polarity along anterior/ posterior, dorsal/ventral or medial/lateral axis is called
-
Question 88 of 90
88. Question
4 pointsExtra-embryonic membranes of the mammalian embryo are derived from
-
Question 89 of 90
89. Question
4 pointsGonads develop from embryonic
-
Question 90 of 90
90. Question
4 pointsCells become variable in morphology and function in different regions of the embryo. The process is