Chapter: Motion in a Plane
0 of 53 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
Information
Subject: Physics
Syllabus: Motion in a Plane
Duration: 30 min.
Read the following instruction carefully.
- There are 30 total questions in this test
- Each question has 4 options out of which only one is correct.
- You will be awarded 4 points for each correct answer and 1 point will be deducted for each wrong answer.
- Try not to guess the answer as there is negative marking.
- Your Score & Rank will be shown after submitting the test.
- In this quiz you are going to check your conceptual knowledge.
You have already completed the Test before. Hence you can not start it again.
Test is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the Test.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this Test:
Your results are here!! for" NPY_11_Phy_03_Motion in a Plane "
0 of 53 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
Your Final Score is : 0
You have attempted : 0
Number of Correct Questions : 0 and scored 0
Number of Incorrect Questions : 0 and Negative marks 0
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
-
Not categorized
You have attempted: 0
Number of Correct Questions: 0 and scored 0
Number of Incorrect Questions: 0 and Negative marks 0
-
PYQ
You have attempted: 0
Number of Correct Questions: 0 and scored 0
Number of Incorrect Questions: 0 and Negative marks 0
-
Dear $form{0} you have completed this test.
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 53
1. Question
0 pointsIf the magnitude of sum of two vectors is equal to the magnitude of difference of the two vectors, the angle between these vectors is
-
Question 2 of 53
2. Question
0 pointsIf \(\begin{align}A=\cos \omega t\widehat{i}+\sin \omega t\widehat{j}\end{align}\)and \(\begin{align}B=\cos \frac{{\omega t}}{2}\widehat{i}+\sin \frac{{\omega t}}{2}\widehat{j}\end{align}\) are functions of time, then the value of \(\begin{align}t\end{align}\) at which they are orthogonal to each other, is
-
Question 3 of 53
3. Question
0 points -
Question 4 of 53
4. Question
0 points\(\begin{align}A\end{align}\) and \(\begin{align}B\end{align}\) are two vectors and \(\begin{align}\theta \end{align}\) is the angle between them. If \(\begin{align}\left| {A\times \left. B \right|} \right.=\sqrt{3}\left( {A\cdot B} \right)\end{align}\) , then the value of \(\begin{align}\theta \end{align}\) is
-
Question 5 of 53
5. Question
0 pointsIf a vector \(\begin{align}2\widehat{i}+3\widehat{j}+8\widehat{k}\end{align}\) is perpendicular to the vector \(\begin{align}4\widehat{i}-4\widehat{i}+\alpha \widehat{k}\end{align}\) , then the value of \(\begin{align}\alpha \end{align}\) is
-
Question 6 of 53
6. Question
0 pointsIf \(\begin{align}\left| A \right.\times \left. B \right|=\sqrt{3}A\cdot B\end{align}\) , then the value of \(\begin{align}\left| {A+\left. B \right|} \right.\end{align}\) is
-
Question 7 of 53
7. Question
0 pointsThe vector sum of two forces is perpendicular to their vector differences. In that case, the forces
-
Question 8 of 53
8. Question
0 pointsIf a unit vector is represented by \(\begin{align}0.5\widehat{i}+0.8\widehat{j}+c\widehat{k}\end{align}\) ,then the value of c is
-
Question 9 of 53
9. Question
0 pointsWhich of the following is not a vector quantity?
-
Question 10 of 53
10. Question
0 pointsThe angle between the two vectors \(\begin{align}A=3\widehat{i}+4\widehat{j}+5\widehat{k}\end{align}\)and \(\begin{align}B=3\widehat{i}+4\widehat{j}-5\widehat{k}\end{align}\) will be
-
Question 11 of 53
11. Question
0 pointsThe resultant of A×0will be equal to
-
Question 12 of 53
12. Question
0 pointsThe angle between \(\begin{align}A\end{align}\) and \(\begin{align}B\end{align}\) is \(\begin{align}\theta \end{align}\). The value of the triple product \(\begin{align}A\cdot \left( {B\times A} \right)\end{align}\) is
-
Question 13 of 53
13. Question
0 pointsThe magnitudes of vectors \(\begin{align}A\text{ },B\end{align}\)and \(\begin{align}C\end{align}\) are \(\begin{align}3,\text{ }4\end{align}\)and \(\begin{align}5\end{align}\) units respectively. If \(\begin{align}A+B=C\end{align}\),the angle between \(\begin{align}\text{A}\end{align}\) and \(\begin{align}\text{B}\end{align}\) is
-
Question 14 of 53
14. Question
0 pointsTwo bullets are fired horizontally and simultaneously towards each other from roof tops of two buildings \(\begin{align}100\,m\end{align}\) apart and of same height of \(\begin{align}200\,m\end{align}\) with the same velocity of \(\begin{align}25\,m/s\end{align}\). When and where will the two bullets collides. \(\begin{align}\left( {g=10m/{{s}^{2}}} \right)\end{align}\)
-
Question 15 of 53
15. Question
0 pointsWhen an object is shot from the bottom of a long smooth inclined plane kept at an angle \( 60{}^\text{o}\) with horizontal, it can travel a distance \(\begin{align}{{x}_{1}}\end{align}\) along the plane. But when the inclination is decreased to \( 30{}^\text{o}\) and the same object is shot with the same velocity, it can travel \(\begin{align}{{x}_{2}}\end{align}\) distance. Then \(\begin{align}{{x}_{1}}:{{x}_{2}}\end{align}\) will be
-
Question 16 of 53
16. Question
0 pointsThe \(\begin{align}x\end{align}\) and \(\begin{align}y\end{align}\) coordinates of the particle at any time are \(\begin{align}x=5t-2{{t}^{2}}\end{align}\) and \(\begin{align}y=10t\end{align}\) respectively, where \(\begin{align}x\end{align}\) and \(\begin{align}y\end{align}\) are in metres and t in seconds. The acceleration of the particle at \(\begin{align}t=2s\end{align}\)is
-
Question 17 of 53
17. Question
0 points\(\begin{align}A\end{align}\) ship \(\begin{align}A\end{align}\) is moving Westwards with a speed of \(\begin{align}10\,km{{h}^{{-1}}}\end{align}\) and a ship \(\begin{align}B\,100km\end{align}\) South of \(\begin{align}A\end{align}\), is moving Northwards with a speed of \(\begin{align}10\,km{{h}^{{-1}}}\end{align}\). The time after which the distance between them becomes shortest is
-
Question 18 of 53
18. Question
0 pointsThe position vector of a particle \(\begin{align}R\end{align}\) as a function of time is given by \(\begin{align}R=4\,\sin \left( {2\pi t} \right)\widehat{i}+4\cos \,\left( {2\pi t} \right)\widehat{j}\end{align}\) where \(\begin{align}R\end{align}\) is in metre, \(\begin{align}t\end{align}\) is in seconds and \(\begin{align}\widehat{i}\end{align}\) and \(\begin{align}\widehat{j}\end{align}\) denote unit vectors along \(\begin{align}x\end{align}\) and \(\begin{align}y-\end{align}\)directions, respectively. Which one of the following statements is wrong for the motion of particle?
-
Question 19 of 53
19. Question
0 pointsA projectile is fired from the surface of the earth with a velocity of \(\begin{align}5\,m{{s}^{{-1}}}\end{align}\) at angle \(\begin{align}\theta \end{align}\) with the horizontal. Another projectile fired from another planet with a velocity of \(\begin{align}3\,m{{s}^{{-1}}}\end{align}\) at the same angle follows a trajectory which is identical with the trajectory of the projectile fired from the earth. The value of the acceleration due to gravity on the planet is \(\begin{align}(in\,m{{s}^{{-2}}})\end{align}\)is \(\begin{align}\left( {given,\,g=9.8\,m{{s}^{{-2}}}} \right)\end{align}\)
-
Question 20 of 53
20. Question
0 pointsA particle is moving such that its position co-ordinates \(\begin{align}\left( {x,y} \right)\end{align}\) are \(\begin{align}\text{(2m,}\,\text{3m)}\end{align}\)at time \(\begin{align}\text{t=0}\end{align}\), \(\begin{align}\text{(6m, 7m)}\end{align}\)at time \(\begin{align}\text{t=2 s}\end{align}\)and \(\begin{align}\left( {13m,\,14m} \right)\end{align}\) at time \(\begin{align}t=5\,s\end{align}\). Average velocity vector \(\begin{align}\left( {{{v}_{{av}}}} \right)\end{align}\)from \(\begin{align}t=0\end{align}\)to \(\begin{align}t=5\,s\end{align}\)is
-
Question 21 of 53
21. Question
0 pointsThe velocity of a projectile at the initial point \(\begin{align}A\end{align}\) is \(\begin{align}(2\widehat{i}+3\widehat{j})\,m/s\end{align}\). Its velocity \(\begin{align}(in\,m/s)\end{align}\)at point \(\begin{align}B\end{align}\)is
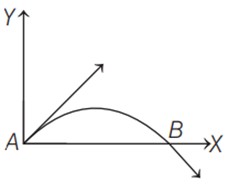
-
Question 22 of 53
22. Question
0 pointsThe horizontal range and the maximum height of a projectile are equal. The angle of projection of the projectile is
-
Question 23 of 53
23. Question
0 pointsA missile is fired for maximum range with an initial velocity of \(\begin{align}20\,m/s\end{align}\). If \(\begin{align}g=10\,m/{{s}^{2}}\end{align}\) , the range of the missile is
-
Question 24 of 53
24. Question
0 pointsA particle has initial velocity \(\begin{align}(3\widehat{i}+4\widehat{j})\end{align}\) and has acceleration \(\begin{align}(0.4\widehat{i}+0.3\widehat{j})\end{align}\). Its speed after \(\begin{align}10\,s\end{align}\) is
-
Question 25 of 53
25. Question
0 pointsA particle of mass \(\begin{align}\text{m}\end{align}\) is projected with velocity \(\begin{align}\text{v}\end{align}\) making an angle of \(\begin{align}45{}^\circ \end{align}\) with the horizontal. When the particle lands on the level ground, the magnitude of the change in its momentum will be
-
Question 26 of 53
26. Question
0 pointsA particle starting from the origin \(\begin{align}(0,0)\end{align}\) moves in a straight line in the \(\begin{align}(x,y)\end{align}\)plane. Its co-ordinates at a later time are \(\begin{align}(\sqrt{3},3)\end{align}\)The path of the particle makes with the \(\begin{align}x-axis\end{align}\)an angle of
-
Question 27 of 53
27. Question
0 pointsFor angles of projection of a projectile at angles \(\begin{align}(45{}^\circ -\theta )\end{align}\) and \(\begin{align}(45{}^\circ +\theta )\end{align}\) the horizontal ranges described by the projectile are in the ratio of
-
Question 28 of 53
28. Question
0 pointsTwo particles are projected with same initial velocities at an angle \(\begin{align}30{}^\circ \end{align}\) and \(\begin{align}60{}^\circ \end{align}\) with the horizontal. Then,
-
Question 29 of 53
29. Question
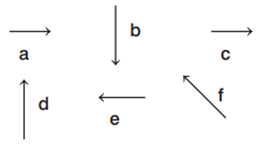
0 pointsTwo particles \(\begin{align}A\end{align}\) and \(\begin{align}B\end{align}\)are connected by a rigid rod \(\begin{align}AB\end{align}\). The rod slides along perpendicular rails as shown here. The velocity of \(\begin{align}A\end{align}\) to the right is \(\begin{align}10m/s\end{align}\). What is the velocity of \(\begin{align}B\end{align}\)when angle \(\begin{align}\alpha =60{}^\circ \end{align}\) ?
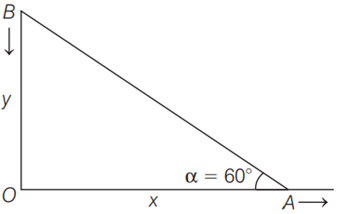
-
Question 30 of 53
30. Question
0 pointsA bullet is fired from a gun with a speed of \(\begin{align}\text{1000}\,\,\text{m/s}\end{align}\) in order to hit a target \(\begin{align}\text{100}\,\text{m}\end{align}\) away. At what height above the target should the gun be aimed? (The resistance of air is negligible and \(\begin{align}g=10\text{ }m/{{s}^{2}}\end{align}\) )
-
Question 31 of 53
31. Question
0 pointsThe position vector of a particle is \(\begin{align}r=(a\,\cos \omega t)\widehat{i}+(a\,\sin \omega t)\widehat{j}\end{align}\). The velocity of the particle is
-
Question 32 of 53
32. Question
0 pointsTwo bodies of same mass are projected with the same velocity at an angle \(\begin{align}30{}^\circ \end{align}\) and \(\begin{align}60{}^\circ \end{align}\) respectively. The ratio of their horizontal ranges will be
-
Question 33 of 53
33. Question
0 pointsThe maximum range of a gun of horizontal terrain is \(\begin{align}16\,km\end{align}\). If \(\begin{align}g=10\,m{{s}^{2}}\end{align}\), then muzzle velocity of a shell must be
-
Question 34 of 53
34. Question
0 pointsThe speed of a swimmer in still water is \(\begin{align}20\,m/s\end{align}\). The speed of river water is \(\begin{align}10\,m/s\end{align}\) and is flowing due east. If he is standing on the south bank and wishes to cross the river along the shortest path the angle at which he should make his strokes w.r.t. north is given by
-
Question 35 of 53
35. Question
0 pointsTwo particles \(\begin{align}A\end{align}\) and \(\begin{align}B\end{align}\), move with constant velocities \(\begin{align}{{v}_{1}}\end{align}\) and \(\begin{align}{{v}_{2}}\end{align}\) . At the initial moment, their position vectors are \(\begin{align}{{r}_{1}}\end{align}\) and \(\begin{align}{{r}_{2}}\end{align}\) respectively. The condition for particles \(\begin{align}A\end{align}\) and \(\begin{align}B\end{align}\) for their collision is
-
Question 36 of 53
36. Question
0 pointsA person swims in a river aiming to reach exactly opposite point on the bank of a river. His speed of swimming is \(\begin{align}0.5\,m/s\end{align}\)at an angle \(\begin{align}120{}^\circ \end{align}\) with the direction of flow of water. The speed of water in stream is
-
Question 37 of 53
37. Question
0 pointsThe speed of a boat is \(\begin{align}5\,km/h\end{align}\) in still water. It crosses a river of width \(\begin{align}1.0\,km\end{align}\) along the shortest possible path in \(\begin{align}15\,\min \end{align}\). The velocity of the river water is (in km/h)
-
Question 38 of 53
38. Question
0 pointsA boat is sent across a river with a velocity of \(\begin{align}8\,km/{{h}^{{-1}}}\end{align}\). If the resultant velocity of boat is \(\begin{align}10km\,{{h}^{{-1}}}\end{align}\), then velocity of river is
-
Question 39 of 53
39. Question
0 pointsA bus is moving on a straight road towards North with a uniform speed of \(\begin{align}50\text{ }km/h\end{align}\). If the speed remains unchanged after turning through \(\begin{align}90{}^\circ \end{align}\) , the increase in the velocity of bus in the turning process is
-
Question 40 of 53
40. Question
0 pointsA particle moving in a circle of radius \(\begin{align}R\end{align}\) with a uniform speed takes a time \(\begin{align}T\end{align}\) to complete one revolution. If this particle were projected with the same speed at an angle \(\begin{align}\theta \end{align}\) to the horizontal, the maximum height attained by it equals \(\begin{align}4R\end{align}\). The angle of projection \(\begin{align}\theta \end{align}\) is then given by
-
Question 41 of 53
41. Question
0 pointsIn the given figure, \(\begin{align}a=15\,m/{{s}^{2}}\end{align}\) represents the total acceleration of a particle moving in the clockwise direction in a circle of radius \(\begin{align}R=2.5\end{align}\). m at a given instant of time. The speed of the particle is
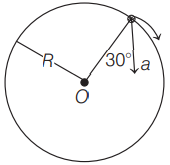
-
Question 42 of 53
42. Question
0 pointsTwo stones of masses \(\begin{align}m\end{align}\) and \(\begin{align}2m\end{align}\) are whirled in horizontal circles, the heavier one in a radius \(\begin{align}\frac{r}{2}\end{align}\) and the lighter one in radius \(\begin{align}r\end{align}\). The tangential speed of lighter stone is \(\begin{align}n\end{align}\) times that of the value of heavier stone when they experience same centripetal forces. The value of \(\begin{align}n\end{align}\) is
-
Question 43 of 53
43. Question
0 pointsA particle moves in a circle of radius \(\begin{align}5\,cm\end{align}\) with constant speed and time period \(\begin{align}0.2\pi s\end{align}\). The acceleration of the particle is
-
Question 44 of 53
44. Question
0 pointsA car runs at a constant speed on a circular track of radius \(\begin{align}100\,m\end{align}\), taking \(\begin{align}62.8\,s\end{align}\)for every circular lap. The average velocity and average speed for each circular lap respectively is
-
Question 45 of 53
45. Question
0 pointsA stone tied to the end of a string of \(\begin{align}1\,m\end{align}\) long is whirled in a horizontal circle with a constant speed. If the stone makes \(\begin{align}22\end{align}\) revolutions in \(\begin{align}44\,s\end{align}\), what is the magnitude and direction of acceleration of the stone?
-
Question 46 of 53
46. Question
0 pointsThe circular motion of a particle with constant speed is
-
Question 47 of 53
47. Question
0 pointsA particle moves along a circle of radius \(\begin{align}\left( {\frac{{20}}{\pi }} \right)m\end{align}\) with constant tangential acceleration. If the velocity of the particle is \(\begin{align}80\,m/s\end{align}\)at the end of the second revolution after motion has begin, the tangential acceleration is
-
Question 48 of 53
48. Question
0 points\(\begin{align}P\end{align}\) is the point of contact of a wheel and the ground. The radius of wheel is \(\begin{align}1m\end{align}\). The wheel rolls on the ground without slipping. The displacement of point \(\begin{align}P\end{align}\) when wheel completes half rotation is
-
Question 49 of 53
49. Question
0 pointsA particle of mass M is revolving along a circle of radius R and another particle of mass m is revolving in a circle of radius r. If time periods of both particles are same, then the ratio of their angular velocities is
-
Question 50 of 53
50. Question
0 pointsWhat is the linear velocity, if angular velocity vector \(\begin{align}\omega =3\widehat{i}-4\widehat{j}+\widehat{k}\end{align}\) and position vector \(\begin{align}r=5\widehat{i}-6\widehat{j}+6\widehat{k}\end{align}\)?
-
Question 51 of 53
51. Question
0 pointsA body is whirled in a horizontal circle of radius \(\begin{align}20\,cm\end{align}\). It has an angular velocity of \(\begin{align}10\,rad/s\end{align}\). What is its linear velocity at any point on circular path?
-
Question 52 of 53
52. Question
0 pointsWhen milk is churned, cream gets separated due to
-
Question 53 of 53
53. Question
0 pointsAn electric fan has blades of length \(\begin{align}30\,cm\end{align}\) measured from the axis of rotation. If the fan is rotating at \(\begin{align}120\,rev/\min \end{align}\), the acceleration of a point on the tip of the blade is